An air circuit breaker (ACB) is an essential electrical device used for protecting circuits from excessive currents and short circuits. This type of breaker operates by using air as an arc extinguishing medium, ensuring that any dangerous arcs are safely eliminated during the interruption of electric flow. The design allows it to respond quickly to faults, making it a popular choice in industrial settings where reliable power distribution is crucial.
ACBs are known for their efficiency and safety features. They can handle high voltage levels and can be adjusted for various trip thresholds, allowing them to cater to different operational needs. By continuously monitoring the electrical flow, these devices provide timely protection, preventing damage to equipment and ensuring the stability of electrical systems.
In this article, readers will gain insights into how air circuit breakers function, their types, and their applications in modern power systems. Understanding these elements will highlight the importance of ACBs in maintaining safe and efficient electrical operations.
What Is an Air Circuit Breaker?
An air circuit breaker (ACB) is an electrical device that protects circuits from overloads and short circuits. It operates by interrupting the electric current flow in a circuit when a fault is detected. This section will explore the core functions, key features, and how it differs from other types of circuit breakers.
Core Function and Importance
The primary function of an air circuit breaker is to protect electrical circuits by interrupting the flow of current during fault conditions. When an overload or short circuit occurs, the ACB detects the anomaly and rapidly disconnects the circuit.
This action prevents damage to electrical equipment and enhances safety in electrical systems. ACBs are particularly important in industrial settings where large machinery and complex electrical systems are used.
Key Functions:
- Overload protection: Prevents damage from excessive current.
- Short circuit protection: Interrupts current flow to avoid severe damage.
- Fault detection: Automatically detects faults and responds quickly.
Key Features and Ratings
Air circuit breakers are designed with several important features to enhance their performance. They include ratings for voltage and current, which dictate their operational capacity.
Typically, ACBs can handle voltages up to 15 kV and current ratings ranging from 800 A to 10 kA. Their components, including contacts and arc extinguishing mechanisms, are designed for durability and reliability.
Notable Features:
- Adjustable trip settings: Customizes responses to fault conditions.
- Electronically controlled: Advanced models utilize microprocessor technology for enhanced precision.
- Environmentally friendly: ACBs do not use oil or gas, reducing environmental risks compared to oil circuit breakers.
Differences from Oil and Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Air circuit breakerss operate differently than oil and vacuum circuit breakers. While oil circuit breakers use oil as an insulating and quenching medium, ACBs rely on air for arc extinction.
This difference in operation leads to distinct advantages. ACBs are generally more compact, making them suitable for various applications. In contrast, vacuum circuit breakers extinguish arcs in a vacuum, which provides high reliability but can limit applications in certain conditions.
Comparison Chart:
| Feature | Air Circuit Breaker | Oil Circuit Breaker | Vacuum Circuit Breaker |
| Arc Quenching Medium | Air | Oil | Vacuum |
| Voltage Range | Up to 15 kV | Varies | Up to 36 kV |
| Environmental Impact | Low | Moderate | Low |
| Size | Compact | Larger | Compact |
These differences can affect the choice of circuit breaker depending on the specific needs of an electrical system.
Components of an Air Circuit Breaker
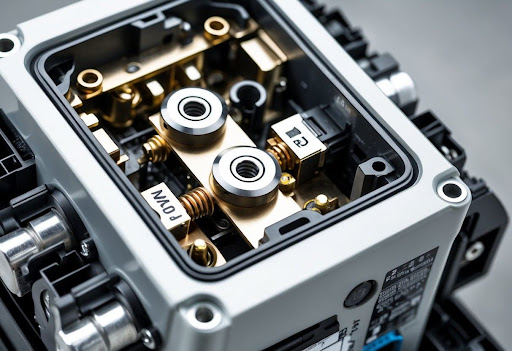
Air circuit breakers are made up of several key components that work together to provide protection to electrical circuits. Each part has a specific role in the functioning of the breaker, ensuring safety and reliability in electrical systems.
Main Contacts and Arcing Contacts
The main contacts in an air circuit breaker are meant to carry the load current during normal operation. They are typically made of a softer alloy that allows for lower impedance, ensuring efficient current flow. These contacts are larger to reduce resistance and heat generation.
Arcing contacts serve a critical role when the circuit breaker opens or closes. They are specifically designed to manage the electrical arc that occurs, thus protecting the main contacts from damage. Often made from a silver-zinc alloy, arcing contacts melt slightly during operation, allowing the arc to form and be safely extinguished in the arc chutes. They must be monitored for wear, as they endure most of the operational stress.
Arc Chutes and Arc Runners
Arc chutes are vital components that help extinguish the electrical arc generated when the circuit breaker operates. They cool down the arc and allow it to be contained within the chute, preventing damage to other components. These chutes often utilize air as a cooling medium and can be designed to handle multiple cycles of arc generation, especially in medium-voltage applications.
Arc runners guide the arc in the chute, ensuring that it is effectively extinguished. These parts are often designed to separate the arc into series arcs, making it easier to cool and extinguish. The effective design of the arc chutes and runners is crucial for maintaining the longevity and reliability of the circuit breaker.
Operating Mechanism
The operating mechanism is responsible for the quick make and break action of the circuit breaker. It comprises several components, including closing springs and trip levers. The closing springs store energy and release it to close the contacts quickly when needed.
The mechanism uses a cradle system that allows the entire breaker to move in and out of its enclosure. This design facilitates maintenance. Interlocking systems may also be integrated to ensure that the mechanism operates safely and that the breaker cannot be accidentally operated while being serviced.
Trip Unit and Auxiliary Contacts
The trip unit is an essential part of the air circuit breaker that monitors electrical currents. It detects conditions such as overloads and short circuits, triggering the mechanism to open the contacts and interrupt the current flow. The trip unit can vary by model, with some incorporating electronic sensing elements for improved accuracy.
Auxiliary contacts work alongside the main components to enable control functions. They are utilized for various tasks, such as activating indicator lights or charging the closing coil. These contacts may also facilitate control circuits and allow for remote operation or monitoring, enhancing the breaker’s usability and functionality.
Working Principle of Air Circuit Breaker
Air circuit breakers operate using a combination of mechanical and electromagnetic techniques to protect electrical systems from overloads and faults. They rely on the interruption of electrical circuits and methods to extinguish the electric arc that may form when the circuit opens. Understanding their core functions is essential for effective usage.
Circuit Interruption and Arc Formation
The primary function of an air circuit breaker is to interrupt the flow of electricity during fault conditions. When the circuit experiences excess current, it triggers the main contacts to open. This action can create an electrical arc due to the high voltage present. The arc forms between the open contacts and has a high temperature. This high temperature can damage components if not controlled properly.
Monitoring the arc voltage is crucial as it directly influences the effectiveness of the circuit interruption. The circuit breaker design must ensure that, once the arc is formed, it can be managed to prevent damage to the breaker and connected devices.
Arc Extinguishing Methods
To protect against damage caused by electrical arcing, air circuit breakers utilize various arc extinguishing methods. One common technique is to cool the arc using air as an extinguishing medium. When the circuit opens, the air can absorb heat from the arc, quickly reducing its intensity.
Additionally, devices like blowout coils help in extending and cooling the arc. These coils produce a magnetic field that increases the arc’s length and promotes cooling. The effectiveness of air as an arc quenching medium makes it a reliable choice for low-voltage applications.
Role of Electromagnetic Forces in Operation
Electromagnetic forces play a significant role in the operation of air circuit breakers. These forces act on the arcing contacts to aid in separating them effectively. When there is an overload, the electromagnetic mechanism energizes, driving the contacts apart swiftly. This rapid opening reduces the duration of the arc formation.
Moreover, the breaker’s design utilizes arcing contacts that are constructed to endure the high currents involved in the process. Their role is to transfer the current from the main contacts during operation, minimizing wear. By effectively managing the electromagnetic forces, air circuit breakers can ensure quick and safe interruption of the circuit to avoid potentially hazardous situations.
Premium electrical and automation equipment
When it comes to electrical and automation equipment, quality is essential. Premium products provide enhanced safety, reliability, and performance. They help prevent hazards that can arise from using lower-quality devices.
Key Features of Premium Equipment:
- Safety Standards: Premium equipment often meets or exceeds international safety standards, ensuring it operates safely and efficiently.
- Durability: Quality materials and robust construction lead to longer lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Performance: High-end devices generally offer better efficiency, which can lead to lower energy costs and improved output.
Investing in premium equipment can significantly reduce risks. For instance, safety features are built-in to prevent electrical faults. Additionally, reputable brands provide proper certifications and guidelines, assuring users of their safety.
Examples of Premium Equipment Providers:
- Gabby Electric: Known for its extensive range of electrical products, Gabby Electric emphasizes quality and safety. Their offerings include automation solutions designed for various industries.
Benefits of Choosing Premium Brands:
- Peace of mind knowing safety is prioritized.
- Better support and warranty options.
- Access to the latest technology and innovations.
Purchasing premium electrical and automation equipment can enhance safety and performance while minimizing the risks associated with lower-quality products.